Information: This is an old - not maintained - article of the AEIOU. In the Austria-Forum you find an updated version of this article in the new AEIOU.
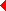
Lorenz, Konrad© Copyright Konrad Lorenz, photo, 1957 Lorenz, Konrad, b. Vienna, Nov. 7, 1903, d. Vienna, Feb. 27, 1989, co-founder of ethology, behavioural scientist, Nobel prize winner for Medicine and Physiology in 1973 (with K. Frisch and N. Tinbergen) for the discovery of character patterns of the greylag goose, son of Adolf Lorenz, brother of Albert Lorenz.1940 Professor at the University of Königsberg, 1948 to 1950 Head of the Institute of Ethology at Gut Altenberg near Vienna, 1954 to 1973 Director of the Max Planck Institute for Behavioural Science at Seewiesen (Germany), from 1973 head of the Department for Animal Sociology at the Institute for Comparative Behavioural Sciences of the Austrian Academy of Sciences; L. especially researched instinctive animal behaviour, the trigger effect following key stimuli as well as the phylogenetic development of innate behaviour. During his last years L. warned repeatedly of the dangers of environmental pollution, in connection with the plebiscite on the Zwentendorf nuclear power plant in 1978 he became a key figure of the emerging environmental protection movement. Works: Der Kumpan in der Umwelt des Vogels, 1935; Die angeborenen Formen möglicher Erfahrung, 1943; Er redete mit dem Vieh, den Vögeln und den Fischen, 1949; So kam der Mensch auf den Hund, 1950; Das sogenannte Böse, 1963; Über tierisches und menschliches Verhalten, 1965; Die Rückseite des Spiegels, 1973; Vergleichende Verhaltensforschung, 1979; Der Abbau des Menschlichen, 1983. Literature: F. M. Wuketits, K. L., Leben und Werk eines großen Naturforschers, 1990. References to other albums:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||